In today’s digital era, maintaining online privacy and security is a growing concern. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a tool that helps protect your internet connection and ensures anonymity online. But what is a Virtual Private Network, how does it work, and what are its pros and cons? This article explores VPN features, types, and everything you need to know.
1. What is a Virtual Private Network?

A Virtual Private Network, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It masks your IP address, ensuring your online activities remain private and protected from hackers, advertisers, and surveillance.
2. Features of a Virtual Private Network
VPNs offer a variety of features, including:
- Encryption: Ensures data is encrypted, protecting sensitive information.
- IP Address Masking: Hides your real IP address, enhancing privacy.
- Secure Remote Access: Allows safe access to private networks from remote locations.
- Kill Switch: Disconnects your internet if the VPN connection drops, preventing data leaks.
- Multiple Server Locations: Enables you to connect to servers worldwide for unrestricted internet access.
3. Types
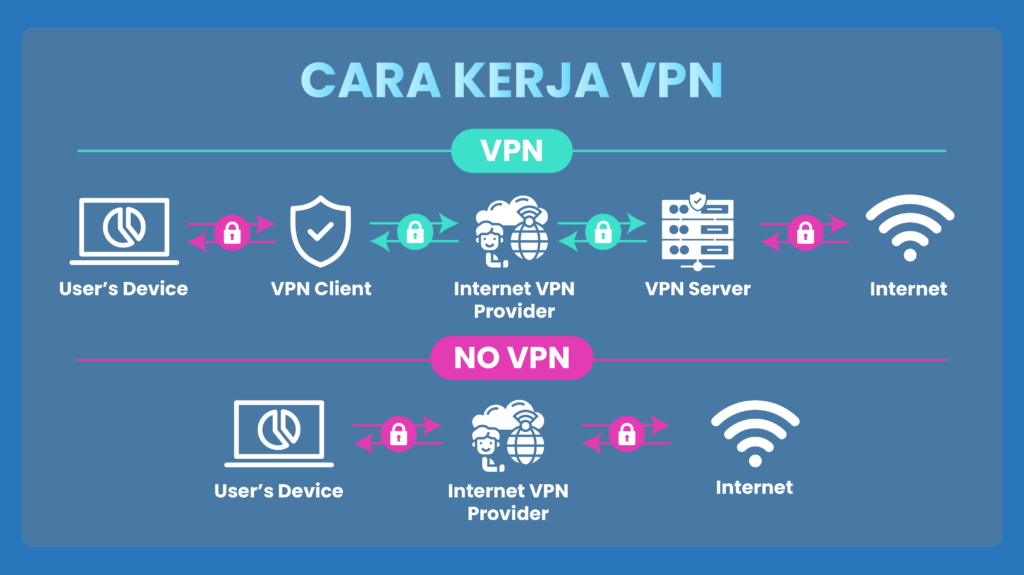
There are several types of VPNs, each serving specific purposes:
- Remote Access VPN: Commonly used by individuals to secure internet connections.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connects two or more networks, often used by businesses.
- Cloud VPN: Provides secure access to cloud-based resources.
- P2P VPN: Optimized for file sharing and torrenting.
- Mobile VPN: Ensures security on mobile devices while switching networks.
4. Advantages of Using
- Enhanced Privacy: Protects your identity and online activity from third parties.
- Secure Public Wi-Fi: Shields data when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Access content that is regionally blocked, like streaming services.
- Improved Online Security: Protects against cyber threats like hacking and phishing.
- Anonymity: Prevents websites from tracking your browsing habits.
5. Disadvantages of Using a Virtual Private Network
- Reduced Speed: Encryption and server distance can slow down internet connections.
- Cost: Premium VPN services can be expensive.
- Trust Issues: Some VPN providers may log user data, compromising privacy.
- Blocked by Some Websites: Certain platforms block VPN connections.
- Configuration Challenges: Setting up advanced VPNs can be complicated for beginners.
6. When Should You Use a Virtual Private Network?
- Traveling Abroad: To access region-restricted content or bypass censorship.
- Online Banking: Protect sensitive data from hackers.
- Remote Work: Securely connect to office networks.
- Torrenting: Safeguard your identity while sharing files.
- Everyday Privacy: Maintain anonymity while browsing.
